sábado, 27 de diciembre de 2008
Muscle and skeletal system
viernes, 14 de noviembre de 2008
Plant tissue
All plants have three basic organs: roots, stems, and leaves. All three organs consist of protective, vascular and ground tissue. Each of which can be further divided into three basic cell types called parenchyma, schlerenchyma, and colenchyma cells.
viernes, 7 de noviembre de 2008
martes, 4 de noviembre de 2008
6 grade Directed Reading
cell wall
1. What is the function of a cell wall?
__________________________________________________________
2. What are the cell walls of plants and algae made of?
__________________________________________________________
3. What are the cell walls of fungi made of?
__________________________________________________________
cell membrane
4. What is a cell membrane?
__________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________
5. What are three types of compounds contained in the cell membrane?
__________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________
6. What two substances control the movement of materials into and out of the cell?
__________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________
CYTOSKELETON
_____ 7. A web of proteins in the cytoplasm is known as the
a. phospholipid. c. cell membrane.
b. cytoskeleton. d. organelle.
8. What are the two functions of the cytoskeleton?
__________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________
NUCLEUS
___ 9. What is the genetic material contained inside a cell’s nucleus?
a. protein c. DNA
b. lipids d. nucleolus
_____ 10. The function of proteins in a cell is to
a. control chemical reactions. c. cover the nucleus.
b. store genetic information. d. copy messages from DNA.
_____ 11. What is the nucleolus?
a. the opposite of the nucleus
b. another name for DNA
c. a network of fibers in the cytoplasm
d. a dark area of the nucleus that stores materials and begins to make ribosomes
ribosomes
12. Organelles that make proteins are called ______________________.
13. Proteins are made of ______________________.
endoplasmic reticulum
14. A system of folded membranes in which proteins, lipids, and other materialsare made is the ______________________.
15. Two forms of endoplasmic reticulum are and ______________________.
Mitochondria
_____ 16. What function does a mitochondrion perform?
a. It breaks down sugar to produce energy.
b. It makes proteins.
c. It breaks down toxic materials.
d. It stores material used to make ribosomes.
17. The site of cellular respiration is the ______________________.
18. Energy produced in mitochondria is stored in a substance called ______________________.
chloroplasts
__ 19. Chloroplasts are organelles that are found in the cells of
a. animals. c. mitochondria.
b. plants and algae. d. all eukaryotic cells.
__ 20. Which process happens inside a chloroplast?
a. production of ATP c. photosynthesis
b. production of DNA d. formation of animal cells
__ 21. Chloroplasts are green because they contain
a. sugar. c. chlorophyll.
b. proteins. d. DNA.
GOLGI COMPLEX
__ 22. The function of the Golgi complex is to
a. produce sugar and water.
b. package and deliver proteins.
c. produce oxygen.
d. trap energy from the sun.
cell compartments
23. A small sac that surrounds material to be moved into or out of a cell is a(n) .______________________
cellular digestion
24. What is a lysosome?
__________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________
25. What is the function of lysosomes?
__________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________
26. What function do vacuoles perform in plant and fungal cells?
__________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________
6 grade The Cell
_____ 1. endoplasmic reticulum _____ 7. Golgi complex
_____ 3. nucleus _____ 9. vesocles
_____ 4. cell membrane _____ 10. DNA
_____ 5. cytoplasm _____ 11. nucleolus
_____ 6. ribosomes _____ 12. chloroplasts
In the space provided, label the structures of the eukaryotic cell drawn below. Include only the structures that you labeled B.

Directed Reading
_____ 1. What is excretion?
- a. the process of digesting food
b. the process of breathing
c. the process of removing waste from the body
d. the process of adding nutrients to the body
2. What is the urinary system?
__________________________________________________________
cleaning the blood
__________________________________________________________
the kidneys as filters
a. one
b. two
c. three
d. four
_____ 5. Which of the following is the job of the nephrons?
a. They remove wastes from the blood.
b. They produce urea.
c. They produce urine.
d. They clean the kidneys.
6. What do the kidneys do?
__________________________________________________________
7. What is urea?
__________________________________________________________
Water in, water out
_____ 8. Why do humans sweat?
a. to cleanse the skin
b. to cool the body
c. to produce saliva
d. to control thirst
9. Why does your body need to excrete as much water as it brings in?
__________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________
10. What does ADH do?
__________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________
11. What effect does a diuretic have on your body?
__________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________
urinary system problems
a. viruses
b. waste materials
c. ADH
d. bacteria
13. How can bacteria get into the bladder and ureters?
__________________________________________________________
14. What can happen if the nephrons are damaged?
__________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________
martes, 28 de octubre de 2008
Urinary system summary seventh grade
Read the following section summary.
• The urinary system removes liquid waste as urine. The filtering structures in the kidney are called nephrons.
• Most of the water in the blood is returned to the bloodstream. Urine passes through the ureter, into the bladder, and out of the body through the urethra.
• Disorders of the urinary system include infections, kidney stones, andkidney disease.
Eukaryotic cells six grade
Read the following section summary.
• Eukaryotic cells have organelles that perform functions that help cells remain alive.
• All cells have a cell membrane. Some cells have a cell wall. Some cells have a cytoskeleton.
• The nucleus of a eukaryotic cell contains the cell’s genetic material, DNA.
• Ribosomes are the organelles that make proteins. Ribosomes are not covered by a membrane.
• The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and the Golgi complex make and process proteins before the proteins are transported to other parts of the cell or out of the cell.
• Mitochondria and chloroplasts are organelles that provide chemical energy for the cell.
• Lysosomes are organelles responsible for digestion within a cell. In plant cells, organelles called vacuoles store cell materials and sometimes act like large lysosomes.
The Urinary System seventh grade
Reinforcement
Annie Apple’s Amazing Adventure
Complete this worksheet after you finish reading the section “The Urinary System.”
Being an apple, Annie is not very good with words. In her story below, she used many terms incorrectly. The incorrect terms have been underlined and numbered. Help Annie by writing the correct term in the corresponding blank provided at the bottom of the page.
Hi, my name is Annie Apple, and I’m, well, an apple! I’ve just been on the strangest adventure, and I thought you’d like to hear about it.
First, this girl took a huge bite out of me and used her teeth to chew me. They call that (1) chemical digestion. While this was happening I got soaked by (2) bile, which breaks down my carbohydrates into simple sugars. Boy, was that -uncomfortable! Then I was swallowed. I went down a long tube called the (3) small intestine, and I ended up in the (4) liver. There, I was bombarded by acid and enzymes, which broke me down further until I was a soupy mixture called (5) amino acids. Next I was released into the (6) large intestine. There I was met by pancreatic juice and (7) saliva. Then I was broken down enough to be partially absorbed into the bloodstream.
After that, I passed into the (8) esophagus, where I had water absorbed from me. At last, what was left of me passed through an opening called the (9) villi. But that’s not the end! The part of me that passed into the bloodstream provided energy to lots of cells before it ended up at the (10) stomach, where it was filtered through tiny (11) bladders and then went out the (12) urethra to be stored in the (13) nephron.
The final leg of my journey was through the (14) ureter to the outside world. Isn’t that an unbelievable adventure?
1.____________________________ 8.__________________________
2.____________________________ 9.__________________________
3.____________________________ 10.__________________________
4.____________________________ 11.__________________________
5. ___________________________ 12.__________________________
6.____________________________ 13.__________________________
7.____________________________ 14.__________________________
vocabulary activity for seventh grade
Vocabulary Activity
Alien Anagrams
After you finish reading the chapter, try this puzzle!
A spaceship full of alien ambassadors has just landed in your backyard. They are very interested in earthling science, especially the study of biological systems. Help them translate their scrambled list of terms. DOOG CLUK!
1. long, straight tube connecting your throat and stomach
2. microscopic filters located in the kidneys
3. large, reddish-brown organ that makes bile, breaks down nutrients, and stores toxins
4. saclike organ that breaks down food into liquid
5. oval organ that sends fluid into the small intestine to chemically digest and neutralize chyme
6. bean-shaped organs that filter blood
7. small, saclike organ that stores bile
8. tube where most chemical digestion occurs
9. tube where liquid waste is changed into solid waste
10. group of organs that work together to digest food
11. group of organs that remove waste from the blood
GAPHOUSES ___________________
HORNPENS ____________________
VIRLE _________________________
SCAMTHO _____________________
SNARPACE ____________________
YIDNEKS ______________________
BALDGLARDLE ________________
LALMS SEENITINT _____________
GELAR NESTIENT ______________
GESTIDIVE SMETYS ____________
YANRIRU TYSMES _____________
vocabulary activity for six grade
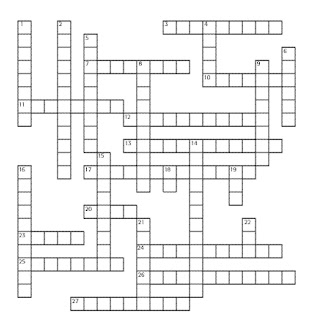
Activity
Vocabulary Activity
Cellular Crosswords
After you finish reading the chapter, use the clues below to complete the crossword puzzle on the next page.
ACROSS
3. the fluid inside a cell
7. the world’s smallest cells
10. the chemical control center of a cell
11. organelle containing digestive enzymes
12. kind of cell that does not have a nucleus
13. organelle that packages and transport materials out of the cell
17. describes an organism that exists as a group of cells
20. A single _____ has everything necessary to carry out life’s activities.
23. scientist who first described cells
24. energy-converting organelle found in plant and algae cells
25. anything that can live independently
26. groups of organs working together to perform particular jobs in the body
27. a structure performing a specific function within a cell
down
1. The cells of plants and algae have a hard _____ _____ made of cellulose.
2. organelles that break down sugar to produce energy.
4. a combination of two or more tissues working together to perform a specific job in the body
5. organelles that make proteins
6. a group of similar cells that perform a common function
8. cells that have a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles
9. sacs that contain materials in a eukaryotic cell
14. barrier between the inside of a cell and its environment
15. dark area inside the nucleus that stores materials that will be used to make ribosomes
16. scientific description of all living things in terms of cells
18. the cell’s delivery system (abbr.)
19. substance that stores energy released by mitochondria
21. a large vesicle that stores enzymes or liquids
22. the cell’s hereditary material
MENU
- SEVENTH GRADE (15)
- SIXTH GRADE (28)



